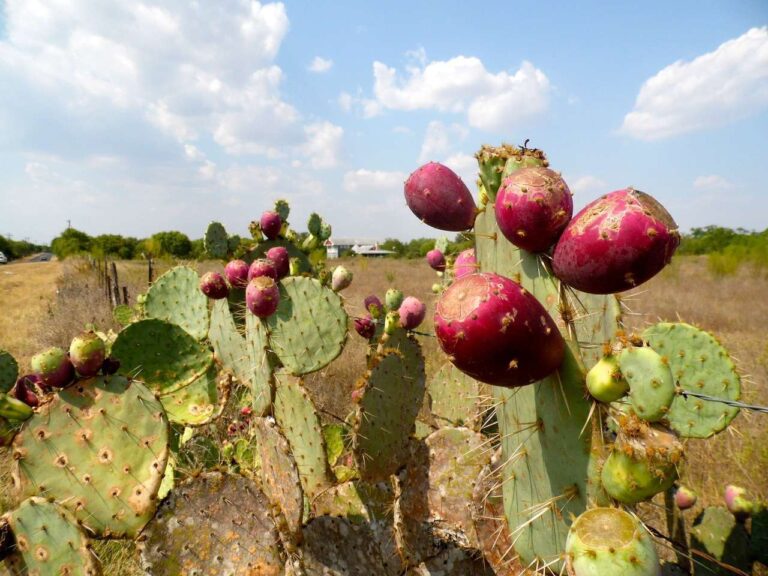
It is the nopal, a bushy plant, with very fleshy stems, of the Opuntia genus, belonging to the botanical family of cacti. It is a symbol in MexicoIt is even present in the national flag. This shrub has nutritional, ecological, industrial, gastronomic and medicinal properties, which have earned it the designation of "the most important plant of the country". green gold.
In terms of nutrition and gastronomy, nopal is rich in fiber, vitamins such as A, C, K, B2 and B6, and minerals such as potassium, calcium and magnesium. It is one of the most traditional foods in the North American country. Its flavor is slightly acidic: when combined with tomato, cilantro, onion, cheese, chili peppers, among others, it can be used to prepare stews, soups, salads, juices, condiments and sweets.
Source of electric power and biofuel
In terms of ecological and industrial use, cactus cultivation is identified as an important source of bioenergy, through its conversion to biogas through the process of decomposition of biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen.
The process begins by cutting the plant, crushing it and introducing it into a hermetically sealed biodigester. It is mixed with water and added to the fermentation process, which produces biogas that can be used immediately to generate electricity.
Similarly, in order for nopal to be used as biofuel, it must undergo cleaning processes to eliminate carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid, obtaining a biogas with 96% of methane, ready to be used in automobiles as a substitute for gasoline. Although biogas from prickly pear cactus contains methane, like natural gas, its production does not require highly complex machinery or devices.
To take advantage of the full potential of this emblematic plant in Mexico, Nopalimex, the first company to work with the production of biogas and electric energy from nopal, was inaugurated at the beginning of 2019. We highlight that this biofuel is 40% cheaper than conventional gasoline, and at the same time it is more environmentally friendly.